In the vast realm of therapeutic interventions for better metabolism, Red Light Therapy (RLT) has emerged as a notable contender, promising a spectrum of health benefits. Often nestled under the broad umbrella of light therapies, RLT is distinct, harnessing the power of specific light wavelengths to interact and positively influence cellular functions in our bodies. One particularly intriguing application of RLT is its potential to enhance metabolism. Metabolism, the intricate symphony of biochemical processes that occurs within us every second, is crucial for our energy, vitality, and overall health.
The science behind how RLT impacts this is rooted in photobiomodulation, where light exposure triggers changes in cellular activity, particularly within our mitochondria. By diving into the biological and scientific nuances of this therapy, we can better understand the profound effects RLT can have on our metabolic health. Join us as we illuminate the intersection of red light, cellular function, and the energetic dance of metabolism.
What is Red Light Therapy (RLT)?
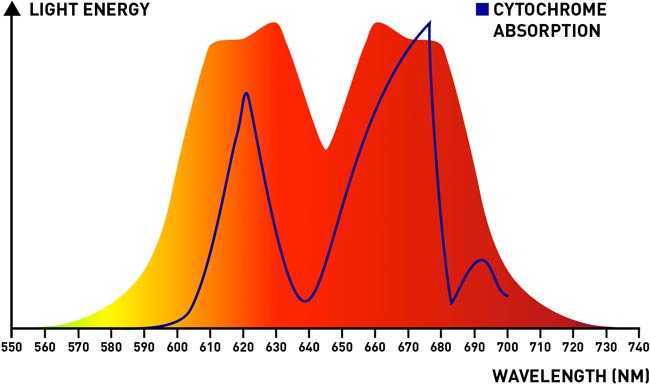
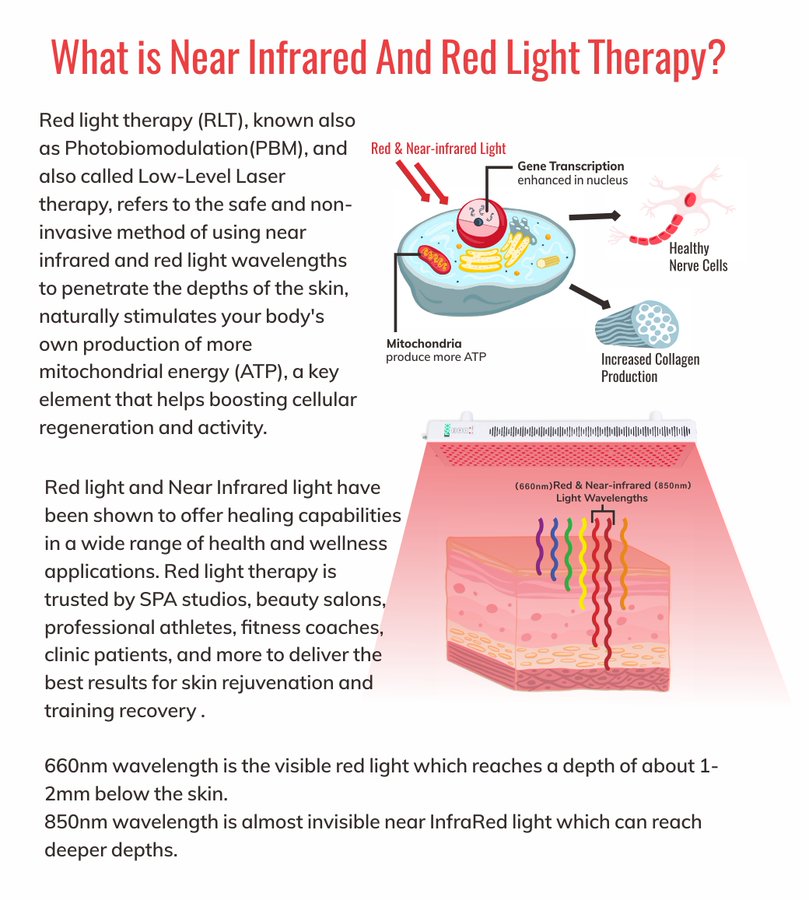
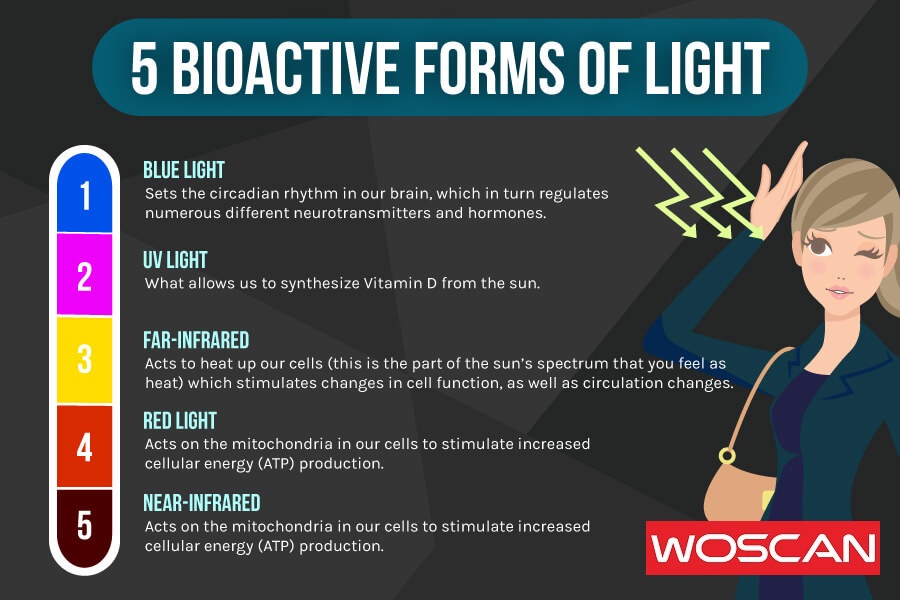
Red Light Therapy (RLT) is a non-invasive therapeutic approach that employs the use of red and near-infrared light wavelengths to elicit beneficial physiological responses in the body. Unlike other forms of light therapy that might target the skin’s surface for aesthetic purposes or use varying wavelengths for different therapeutic effects, RLT specifically harnesses wavelengths in the range of 600nm to 1200nm.
The foundational mechanism of action of RLT is rooted in the science of photo-biomodulation. When our cells, particularly the mitochondria within them, are exposed to these specific wavelengths, they undergo a series of biological reactions. One of the primary technical responses is the stimulation of the cytochrome c oxidase enzyme, a critical component of the cellular respiratory chain. This stimulation leads to an increase in the production of Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP), often termed the ‘energy currency’ of the cell.
The unique feature of RLT is its ability to penetrate skin layers deeper than other forms of light therapy. The red light targets skin tissues, promoting healing and rejuvenation, while the near-infrared light goes even deeper, reaching muscles, bones, and tendons. This depth of penetration is not merely about reaching deeper tissues but also about activating and enhancing cellular functions at various levels.
In essence, Red Light Therapy is a confluence of physics and biology, where specific light wavelengths interact with our cellular machinery, catalyzing a cascade of beneficial physiological processes.
The Scientific Basics: How Does RLT Work?
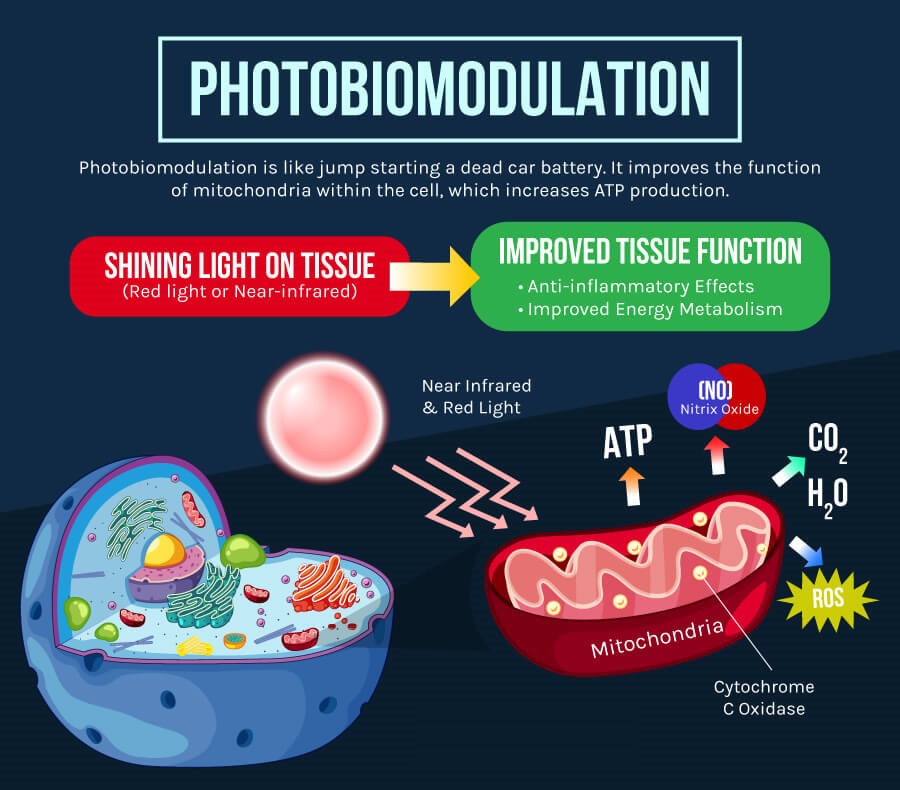
To understand the profound effects of Red Light Therapy (RLT) on the human body, we need to delve deep into the science of photo-biomodulation and cellular biology. At its core, RLT employs the principles of photo-biomodulation (PBM) to stimulate and modify cellular activity in targeted tissues.
A study titled “Mechanisms and Mitochondrial Redox Signaling in Photobiomodulation” articulates the impact of PBM, stating:
“PBM therapy is used to reduce pain, inflammation, edema, and to regenerate damaged tissues such as wounds, bones, and tendons. The primary site of light absorption in mammalian cells has been identified as the mitochondria and, more specifically, cytochrome c oxidase (CCO).”[1]
The mitochondria, play a pivotal role in energy production and cellular health. When exposed to the specific wavelengths of light used in RLT, the cytochrome c oxidase enzyme within the mitochondria becomes activated. This activation is paramount because CCO is a crucial component of the cellular respiratory chain, involved in the last stages of converting our food into usable cellular energy in the form of Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP).
Further supporting these findings, another study titled “Low-level laser (light) therapy (LLLT) in skin: stimulating, healing, restoring” elaborates on the immediate aftermath of photon absorption:
“The photons are absorbed by mitochondrial chromophores in skin cells. Consequently, electron transport, adenosine triphosphate nitric oxide release, blood flow, reactive oxygen species increase, and diverse signaling pathways are activated.”[2]
This quote emphasizes the multi-faceted impact of RLT. Beyond the increase in ATP production, there is a boost in nitric oxide release, which is a vasodilator that enhances blood flow. This increased circulation ensures that oxygen and nutrients are efficiently delivered to cells, promoting faster healing and regeneration. Additionally, the activation of diverse signaling pathways implies a cascade of cellular events that can lead to numerous health benefits, from reduced inflammation to tissue regeneration.
In essence, Red Light Therapy, through the process of photobiomodulation, interacts with the very core of our cells, setting off a chain reaction of events that support and enhance various physiological functions. This scientific foundation is what makes RLT a powerful therapeutic modality with a wide range of applications.
The Connection Between RLT and Metabolism
Metabolism is a complex and continuous orchestration of biochemical processes responsible for converting nutrients into energy, synthesizing the building blocks of cells, and eliminating waste products. Every move we make, every thought we have, and every function our body performs rely heavily on the smooth operation of our metabolic processes.
At the heart of metabolism lie our cells, and more specifically, the mitochondria within these cells. Often described as the cellular ‘powerhouses,’ mitochondria produce Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP), the primary energy currency of the cell. This energy drives almost all cellular and metabolic processes, from muscle contraction to the synthesis of biomolecules.
Red Light Therapy (RLT) has a profound connection with metabolism primarily due to its interaction with these mitochondria. As discussed in the sections above, when specific wavelengths of red and near-infrared light penetrate the body, they are absorbed by chromophores in the mitochondria, specifically the cytochrome c oxidase enzyme (CCO). This interaction leads to an enhanced efficiency of the electron transport chain, a series of reactions vital for ATP production.
When ATP production is optimized, cells receive a more consistent and ample supply of energy. This energy boost can revitalize cells, making them more effective in their respective roles. For instance, muscle cells can recover faster, fat cells can be mobilized more efficiently for energy use, and liver cells can better carry out detoxification processes. This overall enhancement in cellular activity translates to improved metabolic functions.
Furthermore, RLT’s ability to increase nitric oxide release and improve blood flow ensures that nutrients and oxygen are delivered more efficiently to cells, providing the raw materials required for various metabolic processes. In addition, by reducing oxidative stress and potential inflammation, RLT creates a more favorable cellular environment, promoting metabolic health.
To conclude, the intricate relationship between Red Light Therapy and metabolism is anchored in the very basics of cellular biology. By targeting the mitochondria and optimizing ATP production, RLT indirectly enhances the myriad of metabolic processes that govern our health, energy levels, and overall vitality. This scientifically-backed connection offers promising avenues for those seeking holistic methods to boost their metabolic health.
Biological Impact on the Body
Red Light Therapy (RLT), grounded in the science of photobiomodulation, casts a wide net of biological effects on the body. Its ability to influence and enhance cellular functions has been documented in numerous scientific studies, providing a clear picture of the diverse impacts RLT can have.
To truly appreciate the spectrum of effects, we need to delve into the specific biological responses elicited by RLT:
CELL PROLIFERATION AND STEM CELL DIFFERENTIATION
One of the landmark studies titled “Photobiomodulation-Underlying Mechanism and Clinical Applications” sheds light on the significant cellular effects of RLT:
“Photobiomodulation (PBM), also known as low-level laser therapy (LLLT), can induce cell proliferation and enhance stem cell differentiation.”[3]
This aspect is vital for tissue repair and regeneration. By promoting cell proliferation, RLT accelerates the body’s healing processes, ensuring faster recovery from injuries or cellular damage. Additionally, enhancing stem cell differentiation means that the body can more efficiently produce specialized cells necessary for tissue regeneration, such as muscle, bone, or skin cells.
IMPROVED BLOOD FLOW AND TISSUE OXYGENATION
Another study, “Photobiomodulation for traumatic brain injury and stroke,” expounds on the cerebral benefits of RLT, stating:
“In healthy human volunteers (including students and healthy elderly women), PBM has been shown to increase regional cerebral blood flow, tissue oxygenation, and improve memory, mood, and cognitive function.”[4]
By promoting increased cerebral blood flow, RLT ensures that the brain receives a rich supply of oxygen and nutrients. Improved tissue oxygenation is crucial for brain health, cognition, and overall neural function. Moreover, the enhanced memory, mood, and cognitive function are a testament to the holistic benefits of RLT, underscoring its potential in not just physical but also mental well-being.
REDUCTION IN OXIDATIVE STRESS AND INFLAMMATION
RLT has been documented to reduce oxidative stress, a damaging process resulting from an imbalance of free radicals and antioxidants in the body. By curbing this stress, RLT helps prevent cellular damage and premature aging. Additionally, the therapy’s anti-inflammatory properties further promote a healthier cellular environment, which is crucial for metabolic health and overall bodily function.
ENHANCED METABOLIC HEALTH
As previously discussed, the stimulation of the mitochondria and the subsequent boost in ATP production significantly enhance metabolic processes in the body. This impact on metabolism translates to increased energy levels, improved muscle recovery, and potential assistance in weight management.
The biological impact of Red Light Therapy on the body is profound, encompassing cellular, tissue, and organ-level enhancements. These diverse effects, backed by robust scientific studies, make RLT a versatile therapeutic modality with promise in a range of health and wellness applications.
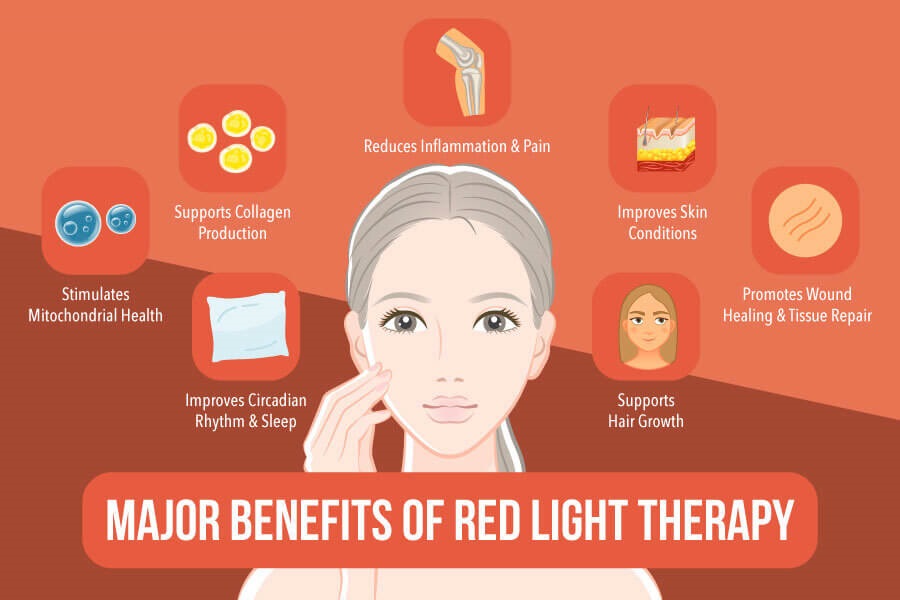
Benefits of Enhancing Metabolism with RLT
Harnessing the power of Red Light Therapy (RLT) to influence metabolism is a burgeoning area of interest, revealing a plethora of advantages that can impact various facets of health and well-being. To fully appreciate the benefits of enhancing metabolism with RLT, it’s vital to understand the intricate dance of physiological and biological processes that the therapy influences. Here are some of the standout benefits:
- Boosted Energy Levels: The fundamental unit of energy in our cells is Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP). RLT’s interaction with mitochondria, particularly with the cytochrome c oxidase enzyme, optimizes the electron transport chain, leading to more efficient ATP production. With higher ATP levels, individuals often experience a surge in vitality and endurance.
- Enhanced Muscle Recovery and Performance: An improved metabolic rate implies faster muscle cell recovery post-exercise. With RLT promoting increased blood flow and tissue oxygenation, muscles receive a rich supply of oxygen and nutrients, which is pivotal for repair and growth. This can lead to better workout performance and reduced recovery times.
- Support in Weight Management: A streamlined metabolic process ensures efficient calorie burning and energy use. RLT’s effect on fat cells encourages the mobilization of stored lipids for energy production, which can assist in weight management when combined with a balanced diet and regular exercise.
- Improved Brain Function: As metabolism is enhanced, the brain benefits from increased blood flow and oxygenation. This can lead to improved cognitive functions, better focus, and clarity, as observed in studies highlighting the cerebral benefits of RLT.
- Better Hormonal Balance: The endocrine system, responsible for hormone production, is intricately linked to metabolic health. By optimizing metabolic functions, RLT indirectly supports hormonal balance, which can have widespread benefits ranging from mood stabilization to improved sleep patterns.
- Support in Detoxification Processes: An efficient metabolism ensures that the body’s detoxification pathways, especially in organs like the liver, function optimally. This means better elimination of toxins, which can lead to clearer skin, improved digestion, and overall better health.
- Reduced Inflammation and Oxidative Stress: A well-functioning metabolic system reduces the potential for inflammation and oxidative stress. As RLT promotes a healthier cellular environment, it aids in curbing these detrimental processes, offering protection against a myriad of health issues they might instigate.
In summation, using Red Light Therapy to enhance metabolism is not just about boosting energy or aiding in weight management. The therapy’s physiological influence reverberates throughout the body, offering a cascade of benefits grounded in cellular biology and metabolic science. As the scientific community continues to uncover the depths of RLT’s potential, individuals stand to gain a comprehensive, holistic tool for health enhancement.
How to Incorporate RLT into Your Routine
Integrating Red Light Therapy (RLT) into one’s daily or weekly regimen can offer an array of health benefits, especially concerning metabolic enhancement. However, for optimal outcomes and safety, it’s crucial to understand the underlying science and the best practices associated with this therapeutic modality. Here’s a comprehensive guide to seamlessly incorporating RLT into your routine:
- Understanding the Science: Before delving into the practice, it’s pivotal to grasp the biological basis of RLT. When specific wavelengths of red and near-infrared light penetrate the skin and underlying tissues, they interact with the mitochondria. This interaction, particularly with the cytochrome c oxidase enzyme, leads to enhanced ATP production, which is the cornerstone of the therapy’s metabolic benefits.
- Choosing the Right Device: Not all RLT devices are created equal. For metabolic enhancement, it’s essential to select a device that emits light at the specific wavelengths proven to be effective for this goal. These wavelengths are 630nm, 660nm, 810nm, 830nm, and 850nm. Ensure that the device you choose is equipped to emit light in these ranges.
- Setting a Consistent Schedule: Consistency is key with RLT. Depending on your goals and the recommendations of health professionals, you might incorporate RLT sessions daily or several times a week. Typically, sessions range from 10 to 20 minutes, but this can vary based on the device’s power and intended outcome. Try our dosing calculator for fast dosing calculations.
- Post-Session Care: After an RLT session, hydrate your body well. Drinking water aids in the metabolic processes and supports the detoxification pathways activated by the therapy.
- Monitor and Adjust: Everyone’s body is unique, and responses to RLT can vary. Keep track of how you feel post-sessions and any noticeable changes in energy levels, mood, and physical health. If needed, adjust the frequency, duration, or intensity of the sessions.
- Integrate with Other Wellness Practices: RLT works synergistically with other health and wellness modalities. Consider integrating RLT sessions with practices like meditation, yoga, or even post-workout routines. This holistic approach can amplify the benefits and offer a comprehensive wellness experience.
- Stay Updated with Research: The field of photobiomodulation and RLT is continually evolving. Staying abreast of the latest research ensures that you’re leveraging the therapy’s full potential and making informed choices about its use. Stay updated with our educational blog.
Incorporating Red Light Therapy into your routine doesn’t have to be daunting. With a solid grasp of the underlying science, the right equipment, and a tailored approach, you can harness the myriad metabolic and holistic benefits that RLT has to offer.
Red Light Therapy (RLT) stands at the forefront of innovative therapeutic modalities, offering a large range of health benefits grounded in cellular biology and metabolic science. The therapy’s ability to stimulate mitochondria, enhance ATP production, and trigger diverse cellular responses is nothing short of revolutionary.
Through the targeted use of specific wavelengths, RLT effectively interacts with the cytochrome c oxidase enzyme within our cellular powerhouses, leading to an optimized metabolic function. Its influence goes beyond mere energy production, resonating through a spectrum of physiological processes from muscle recovery to cognitive enhancement. As we’ve delved deep into the science behind this therapy, its significance in modern health and wellness becomes undeniably evident.
For those seeking a holistic approach to well-being, RLT offers a scientifically-backed avenue to not only enhance metabolism but also to achieve broader health outcomes. Its seamless integration into daily routines and its synergistic potential with other wellness practices make it a versatile tool in one’s health arsenal.
In our rapidly advancing world, where the intersection of technology and biology continually redefines therapeutic boundaries, RLT emerges as a testament to this evolution. As research continues to unearth the depths of its potential, one thing remains clear: Red Light Therapy, with its deep-rooted physiological mechanisms of action, is poised to reshape our understanding of holistic health and healing.
[1] Hamblin MR. Mechanisms and Mitochondrial Redox Signaling in Photobiomodulation. Photochem Photobiol. 2018 Mar;94(2):199-212. doi: 10.1111/php.12864. Epub 2018 Jan 19. PMID: 29164625; PMCID: PMC5844808.
[2] Avci P, Gupta A, Sadasivam M, Vecchio D, Pam Z, Pam N, Hamblin MR. Low-level laser (light) therapy (LLLT) in skin: stimulating, healing, restoring. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2013 Mar;32(1):41-52. PMID: 24049929; PMCID: PMC4126803.
[3] Dompe C, Moncrieff L, Matys J, Grzech-Leśniak K, Kocherova I, Bryja A, Bruska M, Dominiak M, Mozdziak P, Skiba THI, Shibli JA, Angelova Volponi A, Kempisty B, Dyszkiewicz-Konwińska M. Photobiomodulation-Underlying Mechanism and Clinical Applications. J Clin Med. 2020 Jun 3;9(6):1724. doi: 10.3390/jcm9061724. PMID: 32503238; PMCID: PMC7356229.
[4] Hamblin MR. Photobiomodulation for traumatic brain injury and stroke. J Neurosci Res. 2018 Apr;96(4):731-743. doi: 10.1002/jnr.24190. Epub 2017 Nov 13. Erratum in: J Neurosci Res. 2019 Mar;97(3):373. PMID: 29131369; PMCID: PMC5803455.